Image Source: Google
For patients and caregivers dealing with medical conditions that affect the ability to eat or swallow, the use of gastric tubes can be a crucial aspect of treatment. Understanding the different types of gastric tubes, their purposes, and how to care for them is essential for ensuring the well-being of the patient. This comprehensive guide aims to provide information and guidance on navigating the world of gastric tubes.
Types of Gastric Tubes
Nasogastric Tube (NG Tube)
- Inserted through the nose and into the stomach
- Used for short-term feeding, medication administration, or gastric decompression
- Tubes are typically clear in color for easy monitoring
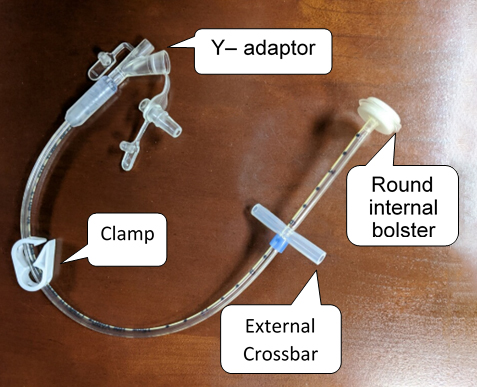
Gastrostomy Tube (G-tube)
- Inserted directly through the abdominal wall into the stomach
- Commonly used for long-term feeding in patients who are unable to swallow
- Available in various types such as PEG (percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy) or surgically placed tubes
Indications for Gastric Tubes
Malnutrition
- Patients who are unable to consume an adequate amount of nutrients orally may require a gastric tube for feeding.
Dysphagia
- Difficulty swallowing due to conditions such as stroke, neurological disorders, or head and neck cancer can necessitate the use of a gastric tube.
Gastric Outlet Obstruction
- Blockage in the stomach or intestines can be relieved through the use of a gastric tube for decompression.
Caring for Gastric Tubes
Cleaning and Maintenance
- Regularly clean around the insertion site with soap and water to prevent infections.
- Check for any signs of redness, swelling, or discharge that may indicate an infection.
- Secure the tube properly to prevent accidental dislodgement.
Feeding and Medication Administration
- Follow the healthcare provider's instructions on how to administer feeds or medications through the tube.
- Use appropriate syringes and liquid formulations to prevent clogging of the tube.
- Flush the tube with water before and after each use to maintain patency.
Monitoring and Troubleshooting
- Monitor the volume and color of gastric contents that are aspirated through the tube.
- Keep track of any signs of tube blockage or dislodgement, such as abdominal pain or leakage around the insertion site.
- Contact the healthcare provider if there are any concerns or issues with the gastric tube.
Potential Complications
Infection
- Proper hygiene practices and regular site care can help prevent infections around the tube insertion site.
Tube Dislodgement
- Accidental removal or displacement of the tube can lead to feeding interruptions or complications.
Gastric Residuals
- Monitoring the volume and content of gastric residuals can help prevent complications such as aspiration pneumonia.
Conclusion
Navigating the world of gastric tubes can be overwhelming for patients and caregivers, but with the right information and guidance, it can become more manageable. Understanding the types of gastric tubes, their indications, proper care practices, and potential complications is essential for ensuring the well-being of the patient. By following the recommendations outlined in this comprehensive guide, patients and caregivers can navigate the world of gastric tubes more effectively and ensure the best possible outcomes for those in need of this vital medical intervention.